The rights of persons with disabilities provide a broad spectrum of inclusiveness. Meanwhile the exclusion of persons with disabilities or mistreatment, calling them by various names such as handicapped, able-bodied, etc. leads to their lack of complete participation in society. So to hinder these barriers and to empower their excellent outgrowth these rights have been created.
You’ve often heard people with disabilities referred to as “the Handicapped”. Did you realise that such references can be incorrect? An individual can be handicapped in a certain statement without being impaired, or have an incapacity yet not be handicapped at many spots. Furthermore a disability is frequently characterised as the failing, misfortune, or disturbance in the ordinary working of physical, social, or psychological cycles.
Hence create trouble in the capacity to learn or change socially, which interferes with an individual’s ordinary development and advancement. Henceforth, a handicap is neither synonym nor unique to people with disabilities, it just alludes to a natural factor that a person finds hard to overcome.
Human Rights-based Chronological Approach to Disability
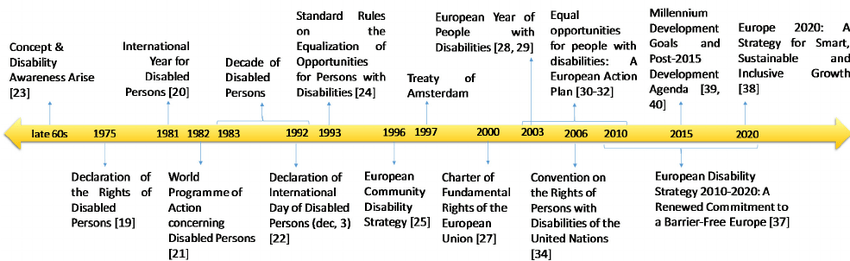
Over the past decade, the understanding and awareness of issues related to people with disabilities have grown. According to WHO “Disability is a vast umbrella of various types of impairments, restrictions to participation, and activity limitations. Additionally, In this way, disability is a complex structure reflecting an interaction with features of a person’s body and the society in which they live. Let us go through the journey of Rights of Persons with Disabilities via road map;

| Year | Events | ||
| late 1960s | Concept of Disability Awareness Arise. | ||
| 1970 | Disability has become a human rights issue. | ||
| 1976 | UN General Assembly proclaimed 1981 to be the “International Year of Disabled Persons” | ||
| 1983-1992 | Marked as a decade of Disabled Persons by the UN. | ||
| 2006 | UNCRPD decided to view persons as “subjects with rights” and not as “objects for charity”. | ||
| 13th Dec 2006 | The Convention on the rights of persons with disabilities and the protocol was adopted at UN Headquarters. | ||
| 30th March 2007 | This is the first Human Rights Treaty of the 21st Century. | ||
| 3rd May 2008 | This Convention for people with disabilities came into force. | ||
| 2010-2020 | A smart and accessible Growth of Disability Rights | ||
Global Scenario For Rights Of Persons With Disabilities

According to ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act), If a person has a mental or physical impairment that creates limitations in life activities, or has a record of that particular impairment.
According to ICIDH (International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities, and Handicaps) 1980, disability is described in three dimensions;
- Impairment: An impairment is a loss or abnormality of physiological, psychological, or anatomical function.
- Disability: It is a lack of activity or any restriction in performing an activity within the range that is considered normal for any human being.
- Handicap: A Handicap is considered a disadvantage for a respective individual due to an impairment that prevents the fulfillment of a role that is normal for an individual.
According to DDA (Disability Discrimination Act), a psychological or physical impairment that has a long-term effect on a person’s day-to-day activities is considered as a person with a disability.
Conventions On The Rights Of Persons With Disabilities

Here I am going to focus on all the 28 articles, starting from Article 3 to Article 30. Convention and the Protocol both came on 13th December 2006. Both of them came into force on 3rd May 2008
Article 3 – It is about the general principles of the state. The key principle of respect for inherent dignity and autonomy of persons with disabilities, inclusion, participation, equality, and accessibility guide of convention obligations.
Article 4 – It is about the general obligations of the state. State parties must revise and review legislation, promote universally designed goods to implement the convention, and consult with persons with disabilities.
Article 5 – It is about equality and discrimination. State parties must prohibit all discrimination on the basis of disability. Persons with disabilities are entitled to equal protection and equal benefit of the law.
Article 6 – It is concerned with women with disabilities. They are subject to various forms of discrimination. State parties must ensure the safety and protection of women empowerment and their complete benefits of fundamental; freedom.
Article 7 – It pays attention to Children with disabilities. State parties must act in accordance with the principle of the best interests of the child, and to ensure the rights of children with disabilities on an equal basis.
Article 8 – It is about raising awareness about disabilities. Parties must increase awareness of the rights of persons with disabilities by using an appropriate mode of communication.
Article 9 – It is about accessibility. All the structures and designs of buildings, transportation systems, information services must be designed and constructed in a way so that they can be used, or reached by persons with disabilities.
Article 10 – The Government must ensure that persons with disabilities also get the same rights as other people for the effective enjoyment of the right to life.
Article 11 – Government or state parties must ensure the safety and protection of civilians at times of natural disaster to secure the safety of persons with disabilities.
Article 12 – The authorities must provide assistance to persons with disabilities in exercising and making decisions.
Article 13 – Persons with disabilities must have all the rights to participate in all the legal proceedings. Authorities must provide training to them for working in the administration of justice, such as prison staff, or police.
Article 14 – Persons with disabilities must get a chance to enjoy the same level of protection against threats to human rights. Similarly This article ensures the liberty and security of a person.
Article 15 – This article focuses on freedom from cruel and inhuman, torture, or degrading punishment/treatment. Accordingly this convention prohibits all scientific and involuntary medical experimentation.
Article 16 – According to this article, if a person with disabilities is mistreated, the authorities must take all measures to ensure appropriate prosecution of mistreatment, the investigation, and the recovery.
Article 17 – The Government must protect the psychological and physical integrity of a person.
Article 18 – This ensures the liberty of movement and nationality. Children with disabilities must get registered at the time of birth in case of disability by birth with name, nationality, etc.
Article 19 – State parties must ensure that and individuals with disabilities can live with complete participation in society with equal access to community services.
Article 20 – Parties must ensure complete access to assistive devices, technologies, mobility aids, and training in mobility skills at affordable cost.
Article 21 – This article supports providing the information in accessible media and formats to make things easy to understand by persons with disabilities.
Article 22 – The privacy of persons with disabilities must be honored and protected.
Article 23 – They have the right to choose how, where, and with whom they want to live.
Article 24 – To provide inclusive education and learning process, including access to all the primary, secondary, tertiary, and vocational institutions.
Article 25 – Authorities must ensure that an individual with disabilities has access to all the health services especially the ones that are gender-sensitive Health care services must be free and by their informed consent.
Article 26 – This article ensures that persons with all forms of disabilities get complete involvement in all aspects of life such as mental, vocational, social, and physical.
Article 27 – Everybody has a right to work. Therefore this article supports the right to work and takes appropriate steps to promote employment in the private sector. Authorities are called to employ persons with disabilities in the public sector.
Article 28 – This Article makes sure that people with disabilities have adequate shelter, drinking water, clothing, and food. They have all social safety nets.
Article 29 – All feasible steps must be taken to encourage and facilitate the participation of persons with disabilities in Government and other civic activities such as stand and participation in elections, rights to vote, etc.
Article 30 – Person with disabilities has a right to play, participate in sports. Authorities must ensure their accessible participation and availability of cultural facilities such as theater, museums, and monuments in accessible formats.
Indian Scenario For Rights Of Persons With Disabilities

In India, an act came into force in 2016 known as The Rights Of Persons With Disability, 2016. This act replaced The Persons With Disabilities Act, 1995. Furthermore The 1995 Act was focusing on equal opportunity protection of rights and Full Participation. In The 2016 Act, three sections are defined;
Section 2(r)- This section covers the person with benchmark disability. This means a person with not less than 40% of a specific disability if the disability cannot be measured in measurable terms that are considered as certified by the certifying agency.
Section 2(s)- The person with a disability means a person with long terms psychological, physical, sensory, and intellectual impairment with barriers that hinders their complete participation in society with others.
Section 2(t)- The persons with disabilities with high support needs, come under this section. This is a part of Section 58(Procedure For Certification).
Conventions On The Rights Of Persons With Disabilities

The Act discusses various rights and responsibilities that are covered under various disabilities such as;
Section 3- It discusses equality and nondiscrimination.
Section 4- It is about the rights of children with disabilities.
Section 5- It covers the rights of community life.
Section 6- It is for protection from cruelty and inhuman treatment.
Section 7- It is on protection from abuse violence, and exploitation of persons with disabilities.
Section 8- Safety and Protection of Person with disability.
Section 9- This covers Home and the family.
Section 10- Reproductive Rights Of Persons with Disability.
Section 11- Accessibility in Voting for persons with disabilities.
Section 12- This section is focused on Justice for people with disabilities. It ensures the accessibility of Justice.
Section 13- Complete Legal Capacity of Persons with disabilities.
Section 14- Provision for guardianship.
Section 15- This section covers the Designation of Authorities to support persons with disabilities.
Henceforth along with these sections, there are some more rights available for an individual with a disability such as rights of education, skill development, health, employment, and rehabilitation, etc.
SPECIAL PROVISIONS FOR PERSONS WITH BENCHMARK DISABILITIES

- The safety and protection of a person with a disability are the responsibilities of the government and to ensure that they take advantage of their rights with others equally.
- Special schemes and development programs.
- Incentives to employers in the private sector.
- Multiple reservations are there for an individual with a disability such as in there are a minimum of 5% reservations and for government jobs, there is a minimum of 4% reservations, for higher educations and in poverty schemes, there are 5% reservations.
- In the field of education if the disability falls in the age group of 6 to 18 years then he has the right to free education and if any institute falls under the Government of India then inclusive education is provided to the children with disabilities.
- National funds are provided for persons with disabilities.
- This act provides a grant of guardianship to choose by the person with a disability as per their wish or choice.
Penalties For Offences Of Rights For Persons With Disabilities

Under The Act 2016, Sections 89-95 are for the penalties for offences of rights for persons with disabilities. Additionally Any violation of these acts is punishable with imprisonment of 6 months to 5 years, a fine from Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 5,00,000, or both if the violation is more severe. Simultaneously, if the violation is covered under any other central act the greater degree of punishment shall be considered.
Summary

Now we have learned a lot about the human rights of persons with disabilities. There was a question in the beginning in everybody’s mind that,” What is the need of a Convention Treaty or a separate community for their Rights?” As we all know people around the world face discrimination and the denial of human rights. On the whole, these Authorities or Acts are made and came into force to address this concern worldwide.Moreover the Convention is a human rights treaty that sets out how to make our world disability-inclusive. A committee of 18 persons from UN member countries monitors whether these rights are properly upheld.
Thus all the rights are focused on the complete involvement and participation of people with disabilities in making decisions that affect their lives. For instance they must have their dignity respected and their voices heard and call for equality for women and girls. Society’s barriers are the problems not the individuals with impairments. Henceforth these rights help in removing the barriers and preventing people with disabilities from participating.
Click on below link to reach us for conducting a Disability Awareness Program for your employees
Let’s all join the fight of a world where no one is left behind and start building Equity which is the concept of fairness.